Navigating Industry 4.0: A guide for the rest of us
Back in 2011, a term popped up at a big tech fair in Hannover, Germany, that was set to change the game for factories and businesses everywhere. This term was “Industry 4.0,” (or “Industrie 4.0” in its original context) and it was part of Germany’s high-tech strategy to make their manufacturing smarter.
What started as a fancy way to say “let’s make our factories more digital” has gained traction all across the world and grown into something much bigger. Now, Industry 4.0 is about shaking up how every part of an industrial business runs, from the front desk all the way to the delivery truck.
See also: Podcast: Cybersecurity landscape and SEC rules for 2024
See also: New SEC Reporting Requirements and Your Cyber Defenses
Imagine a world where the pieces of your business talk to one another—your ordering system knows what’s happening on the factory floor, your delivery trucks know what the weather’s like in real-time, and your customer service team knows exactly what your customers want before they even ask. That’s the dream of what most companies view as Industry 4.0. But here’s the kicker: Jumping into Industry 4.0 without really thinking about how to do it right can be a bit like trying to run before you can walk.
The big idea behind Industry 4.0 has grown a lot since 2011. It’s not just about making things more efficient or effective. It’s about reimagining how we do everything in business. This means looking at our old processes with fresh eyes and asking: “Is there a better way to do this with the new tech we have?”
See also: Microsoft hack tests new SEC disclosure rules
But here’s the thing—Industry 4.0 is kind of like a never-ending road trip as it really describes the era we are living in right now: the Fourth Industrial Revolution. This means there is no “You Are Here” sign because the landscape keeps changing based on new technological developments, economic conditions, and overall digital maturity.
New gadgets, gizmos, and ways of doing things pop up all the time. The businesses that are going to come out on top are the ones that see this not as a chore but as an adventure. They’re the ones always on the lookout for new ideas and ways to make things better, faster, and cooler for their customers.
When companies dive into the world of Industry 4.0, there’s a common trap they often fall into: focusing almost exclusively on the operational side of things. It’s easy to get caught up in the allure of streamlining production or integrating the latest tech into manufacturing processes. However, the true power of Industry 4.0 lies in its ability to transform not just how we make things, but how we manage every aspect of our businesses.
See also: Sustainability, traceability, visibility: New rules and tools for complex manufacturing
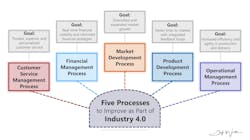
To fully harness the potential of this digital revolution, it’s crucial to consider five key processes: customer service management, financial management, market development, product development, and operational management. Each of these areas offers a unique opportunity to innovate and improve, driving towards a more connected, efficient, and customer-focused business.
The Customer Service Management Process
This process is all about ensuring your customers feel valued and understood. The aim is to provide trusted, superior, and personalized service that keeps them coming back.
Here’s an example: Integrating customer service platforms with IoT devices can provide service teams with real-time data on product performance, leading to proactive customer support.
For instance, if a “smart” device or “smart” machine in a customer's manufacturing facility starts malfunctioning, the service team can be alerted automatically, initiating contact with the customer to resolve the issue before it escalates. This proactive approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also feeds valuable data back into the product development process, informing future improvements.
The Financial Management Process
Financial management in the Industry 4.0 era is about gaining real-time visibility into your finances and making informed decisions. The goal is to ensure financial strategies are data-driven, optimizing for profitability and sustainability.
See also: eHandbook: The Smart Industry 2024 Crystal Ball Report
Here’s an example of that process: By integrating financial management software with other business systems (such as sales, procurement, and inventory management), companies can achieve a unified view of their financial health.
This integration allows for automated budgeting and forecasting, which can adjust in real-time based on sales data and inventory levels, ensuring financial strategies are always aligned with current business realities.
The Market Development Process
This process focuses on identifying and entering new markets or expanding in existing ones. The goal is diversified and expanded market growth, ensuring the company’s offerings meet the evolving needs of a global audience.
Here’s a practical example: Utilizing advanced analytics to cross-reference customer service data, social media feedback, and global sales trends can uncover untapped market opportunities or emerging customer needs.
This holistic view enables businesses to tailor market development strategies that are informed by real-world data, ensuring efforts are targeted and effective.
The Product Development Process
In Industry 4.0, product development is about speeding up the journey from idea to market, incorporating customer feedback directly into the design process. The goal is to achieve faster time-to-market with products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
See also: Tailoring OT-IT convergence for enhanced data access, management
Here’s an example of that process: Employing agile development methodologies that incorporate feedback loops from customer service insights, financial performance data, and market analysis can significantly enhance product relevance and appeal.
For example, if customer service trends indicate a common issue or request, product development can prioritize these features in the next iteration, supported by financial analysis to ensure profitability.
The Operational Management Process
Operational management is the backbone of Industry 4.0, focusing on making production and delivery as efficient and agile as possible. The goal is to leverage digital technologies to streamline operations, reducing waste and increasing flexibility.
Here’s a practical example: Implementing smart manufacturing systems that are integrated with supply chain management tools and predictive analytics can optimize production schedules based on real-time demand forecasts and supply chain constraints.
See also: New research sees buy-in for digital transformation growing among manufacturing stakeholders
This not only improves operational efficiency but also ensures that production is closely aligned with market needs and financial objectives, reducing waste, and enhancing responsiveness to market changes.
By focusing on these five processes, companies can ensure they’re not just upgrading their technology, but transforming their entire business to thrive in the digital age. Industry 4.0 isn’t just about making things; it’s about making things better, smarter, and more in tune with what customers want and need.
The journey into Industry 4.0 is like heading into uncharted territory. It’s exciting, a bit scary, but full of potential. The key is to keep moving, keep learning, and never be afraid to try something new. After all, the businesses that are going to win the future are the ones that are always evolving, just like Industry 4.0 itself. So, what are you waiting for? Let’s hit the road.
About the Author

Jeff Winter
Jeff Winter is senior director of industry strategy for manufacturing with Hitachi Solutions. Winter is active in the Industry 4.0 community. He is on the international board of directors for the Manufacturing Enterprise Solutions Association and the International Society of Automation. He’s also a U.S.-registered expert for the International Electrotechnical Commission as a member of TC 65 and a smart manufacturing adviser to CESMII.